In today’s digital landscape, ransomware has emerged as one of the most pervasive and damaging cyber threats facing organizations of all sizes. As cybercriminals continue to refine their tactics, Australian businesses find themselves increasingly in the crosshairs. The stakes couldn’t be higher: when ransomware strikes, organizations face not just financial demands but operational paralysis, reputational damage, and potentially devastating data loss.
The Growing Ransomware Threat in Australia
Australia has witnessed a concerning upward trend in ransomware attacks. According to the Australian Cyber Security Centre’s (ACSC) Cyber Threat Report 2022–231, ransomware remains the most destructive cybercrime threat in 2022–23 to Australian entities. ASD recorded 118 ransomware incidents – around 10 per cent of all cyber security incidents.
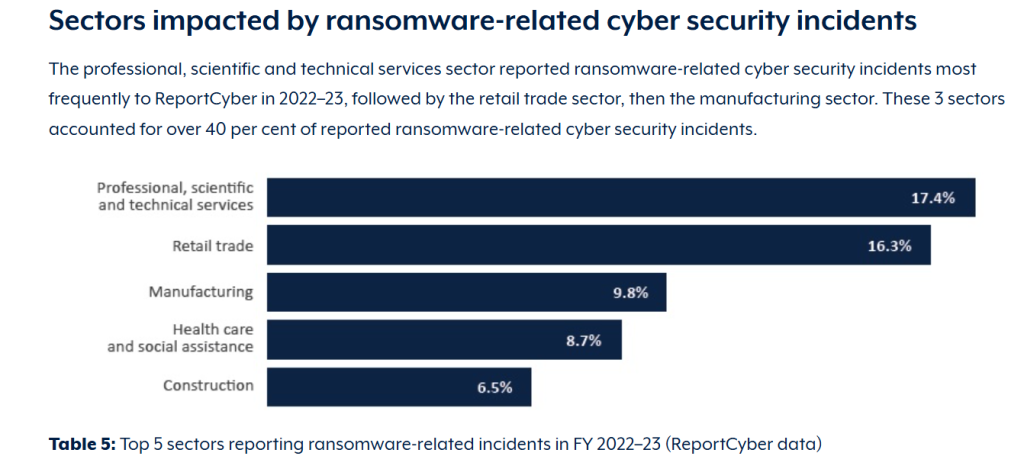
According to the report, the scientific and technical services, retail trade, and manufacturing sectors remain particularly vulnerable, all of which accounted for over 40 per cent of reported ransomware-related cyber security incidents. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) face disproportionate risk, with many lacking comprehensive backup solutions despite being targeted in attacks.
Understanding the Ransomware Kill Chain
Ransomware attacks don’t simply happen; they follow a predictable sequence, for instance, as detailed by Microsoft in its threat actor update titled “Storm-0501: Ransomware attacks expanding to hybrid cloud environments2” — a kill chain that offers multiple opportunities for prevention and intervention:
- Initial Access: Typically via phishing emails, compromised credentials, or exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities
- Execution: Malicious code runs and begins the encryption process
- Persistence: Attackers establish methods to maintain access
- Lateral Movement: Spreading throughout the network to maximize impact
- Data Exfiltration: Stealing sensitive data before encryption (double extortion)
- Encryption: Rendering files and systems inaccessible
- Ransom Demand: Requesting payment for decryption keys
Understanding this progression reveals why robust backup and recovery systems form a critical layer in any comprehensive defense strategy.
The 3-2-1-1-0 Backup Strategy
While the classic 3-2-1 backup rule (three copies, two different media types, one off-site) has served organizations well, today’s ransomware landscape demands an enhanced approach. Enter the 3-2-1-1-0 strategy:
- 3 copies of your data (primary plus two backups)
- 2 different storage media types
- 1 copy stored off-site
- 1 copy stored offline or air-gapped
- 0 errors upon verification and testing
The additional elements — air-gapped storage and rigorous verification—specifically address ransomware’s ability to target connected backup systems and the critical need for recovery assurance.
Building a Ransomware-Resilient Backup Architecture
A truly resilient backup architecture incorporates several key components:
1. Immutable Storage Solutions
Immutable backups cannot be altered or deleted once written, even by administrators, for a specified retention period. This technology prevents attackers from tampering with backup data, effectively neutralizing a common ransomware strategy. For instance, Microsoft’s analysis, “Generally available: Immutable vaults with Azure Backup3“, walks us through its immutable vaults with Azure Backup, which it explains ensures that backup data cannot be modified or deleted, even by administrators, for a specified retention period. This feature enhances ransomware resilience by preventing attackers from tampering with stored backups.
Modern immutable storage solutions employ write-once-read-many (WORM) technology, ensuring that once data is written, it remains unchanged until the retention period expires. Implementation options include:
- Cloud-based immutable storage services
- On-premises WORM-capable storage systems
- Specialized backup appliances with immutability features
2. Air-Gapped Protection
According to IBM’s explanation of Air Gap, “What is an air gap?4“, Air-gapped systems maintain physical or logical separation from production networks, creating a crucial barrier that most ransomware cannot cross. Effective air-gapping approaches include:
- Physical Air Gaps: Completely disconnected backup systems, such as tape drives or removable storage that’s only connected during backup windows
- Logical Air Gaps: Network segmentation with strict access controls and one-way data flow
- Cloud Air Gaps: Specialized cloud services that implement logical separation and immutability
3. Automated Testing and Verification
Untested backups represent an unknown risk. Automated verification ensures backups are not only created but viable for recovery:
- Scheduled recovery testing of critical systems
- Integrity checks to verify data hasn’t been corrupted
- Documentation of recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs)
- Identification of recovery bottlenecks before a crisis occurs
Google’s Google Cloud Well-Architected Framework, titled “Perform testing for recovery from data loss5,” emphasizes the importance of scheduled recovery testing, integrity checks, and monitoring recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to ensure data resilience.
4. Encryption and Access Controls
While protecting backups from encryption is paramount, so too is protecting them from unauthorized access:
- Encrypt backup data both in transit and at rest
- Implement multi-factor authentication for backup management systems
- Apply the principle of least privilege to backup administration
- Maintain separate credentials for backup systems
Microsoft in its Microsoft Defender for Cloud Blog post, “Security Control: Encrypt data in transit6,” stresses the need for encrypting backup data in transit and at rest, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), and enforcing least privilege access for backup management.
Integrating Backup Strategy with Broader Security Measures
Effective ransomware resilience integrates backup systems with:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Early detection of ransomware activity
- Network Segmentation: Containing potential infections
- Vulnerability Management: Reducing attack surface
- Security Awareness Training: Preventing initial compromise
- Incident Response Planning: Ensuring rapid recovery execution
Developing an Effective Recovery Plan
Even the best backup strategy falls short without a comprehensive recovery plan. Key components include:
- Prioritization: Identifying critical systems and data for expedited recovery
- Documentation: Detailed, accessible recovery procedures
- Role Assignment: Clear responsibilities during recovery operations
- Communication Protocols: Internal and external communication plans
- Regular Drills: Practiced, timed recovery exercises to identify gaps
Case Study: The City of Onkaparinga Recovery
In late 2019, the City of Onkaparinga7, South Australia’s largest metropolitan council, faced a severe ransomware attack. The Ryuk ransomware, a highly sophisticated strain, infiltrated their systems, causing a complete shutdown of servers, email systems, and VoIP phones. Community services, including libraries and support hubs, were also disrupted.
Key recovery actions included:
- Collaboration with experts: The council worked with cybersecurity firms like Sophos and Compnow to manage the crisis.
- 24/7 monitoring: Managed Threat Response (MTR) service became a critical part of their recovery and future prevention strategy.
- Post-incident improvements: The council enhanced its technology and business environment to prevent future attacks.
This case underscores the importance of expert partnerships and proactive measures in managing ransomware incidents.
Conclusion
As ransomware attacks continue to evolve in sophistication and frequency, a well-designed backup and recovery strategy remains the ultimate insurance policy. By implementing the 3-2-1-1-0 approach, embracing immutability and air-gapping, and integrating backup systems with broader security measures, Australian organizations can dramatically improve their ransomware resilience.
Remember that effective backup strategies aren’t static—they require regular testing, updating, and alignment with evolving threats and business requirements. The most successful organizations view backup not merely as a technical function but as a critical business continuity capability deserving of appropriate investment and attention.
By taking these proactive steps, your organization can face the ransomware threat with confidence, knowing that when prevention fails, recovery remains within reach.
References
- Australian Signals Directorate, “ASD Cyber Threat Report 2022–23”, 2023 https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/view-all-content/reports-and-statistics/asd-cyber-threat-report-july-2022-june-2023 ↩︎
- Microsoft, “Storm-0501: Ransomware attacks expanding to hybrid cloud environments”, 2024 https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/blog/2024/09/26/storm-0501-ransomware-attacks-expanding-to-hybrid-cloud-environments/ ↩︎
- Microsoft, “Generally available: Immutable vaults with Azure Backup”, 2023 https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/azuregovernanceandmanagementblog/generally-available-immutable-vaults-with-azure-backup/3782466 ↩︎
- IBM, “What is an air gap?”, 2024
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/air-gap ↩︎ - Google, “Perform testing for recovery from data loss”, 2024 https://cloud.google.com/architecture/framework/reliability/perform-testing-for-recovery-from-data-loss ↩︎
- Microsoft, “Security Control: Encrypt data in transit”, 2021 https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/microsoftdefendercloudblog/security-control-encrypt-data-in-transit/2201008 ↩︎
- Surviving a shocking ransomware attack: Lessons from the City of Onkaparinga https://www.compnow.com.au/case_study/surviving-a-shocking-ransomware-attack-lessons-from-the-city-of-onkaparinga/
↩︎
At Christian Sajere Cybersecurity and IT Infrastructure, we safeguard your data with resilient backup and recovery solutions. Stay secure, stay operational, and recover confidently from ransomware threats.
Related Blog Posts
- Cybersecurity Essentials for Startups: Safeguarding Your Business from Digital Threats
- Insider Threats: Detection and Prevention Strategies
- Securing Microsoft 365 Email Environments: A Comprehensive Guide
- Crisis Communication During Security Incidents: A Strategic Approach
- Building a Security Operations Center (SOC): Key Components
- Implementing Single Sign-On: Pros, Cons, and Best Practices
- Continuous Compliance Monitoring Through Automation