In an era where cyber threats are escalating at an unprecedented pace, small and medium businesses (SMBs) face a critical challenge: securing their operations without breaking the bank. Globally, research from Microsoft Security in “New research: Small and medium business (SMB) cyberattacks are frequent and costly”1 reveals that 1 in 3 small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) were hit by cyberattacks in the past year. The average cost per incident was nearly $254,445, with some businesses facing losses as high as $7 million.
In Australia, the Australian Signals Directorate’s (ASD) Annual Cyber Threat Report 2023-20242 shows that small businesses lost an average of $49,600 per cyber incident, reflecting an 8% year-over-year increase. These numbers underscore the urgent need for tailored cybersecurity strategies, especially for smaller enterprises with limited resources.
The global cybersecurity landscape has reached a tipping point. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 20243, the average cost of a data breach has reached $4.9 million globally, marking a 10% increase from the previous year and the highest total ever recorded. This stark reality presents a dilemma for resource-constrained organizations: how can they implement robust security measures without exhausting their limited budgets?
The answer lies in strategic, cost-effective security solutions that maximize protection while minimizing financial burden. This comprehensive guide explores practical, budget-friendly approaches that can significantly enhance your organization’s security posture without compromising operational efficiency or financial stability.
Understanding the Current Threat Landscape
The Rising Tide of Cyber Threats
The cyber threat environment has evolved dramatically, with attackers becoming more sophisticated and persistent. Microsoft’s Digital Defense Report 20244 indicates that organizations worldwide face approximately 600 million cyberattacks daily. This staggering statistic underscores the reality that no organization, regardless of size, is immune to cyber threats.
The Australian Cyber Security Centre’s (ACSC) Annual Cyber Threat Report 2023-20245 reveals that cybercrime continues to surge, with the Australian Cyber Security Hotline receiving over 36,700 calls in the past year, representing a 12% increase from the previous year. More than 1,100 cybersecurity incidents were reported to the ACSC, highlighting the persistent nature of these threats.
The SMB Vulnerability Gap
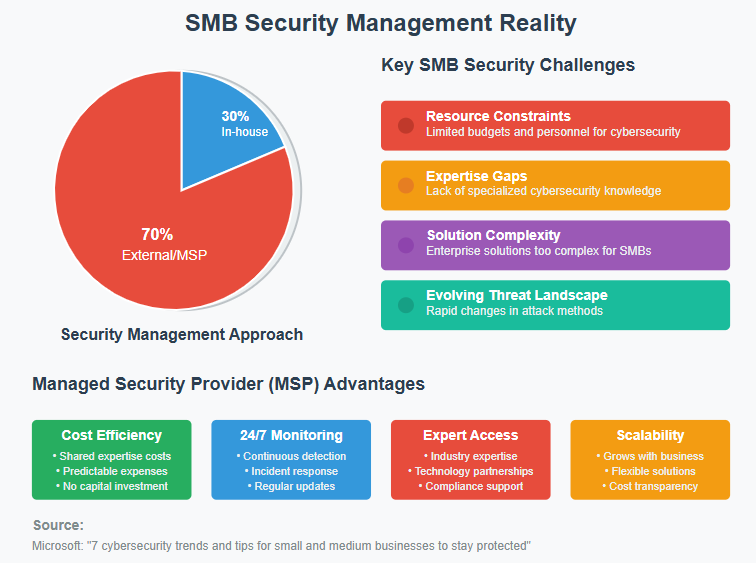
Small and medium businesses face unique challenges in the cybersecurity landscape. Unlike large enterprises with dedicated security teams and substantial budgets, SMBs often operate with limited resources and expertise. Analysis by Microsoft in “7 cybersecurity trends and tips for small and medium businesses to stay protected”6 shows that less than 30% of SMBs manage their security in-house, with the majority relying on external security consultants or service providers.
This vulnerability is compounded by several factors:
- Resource constraints: Limited budgets and personnel dedicated to cybersecurity
- Expertise gaps: Lack of specialized cybersecurity knowledge within the organization
- Complexity of solutions: Traditional enterprise security solutions often too complex for SMB environments
- Evolving threat landscape: Rapid changes in attack methods and techniques
Core Principles of Cost-Effective Security
1. Risk-Based Approach
The foundation of cost-effective security lies in understanding and prioritizing risks. Organizations should focus their limited resources on protecting their most critical assets and addressing the highest-probability threats. This approach ensures maximum security impact per dollar spent.
2. Layered Defense Strategy
Rather than investing in expensive, single-point solutions, successful SMBs implement a layered defense strategy. This approach combines multiple, complementary security measures to create a robust security posture without requiring substantial individual investments.
3. Automation and AI Integration
Organizations that extensively deployed security AI and automation saved an average of $2.2 million per breach compared to those that didn’t deploy these technologies, according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 20247. For SMBs, this translates to significant cost savings through reduced manual security operations and improved threat detection capabilities.
Budget-Friendly Security Solutions
Essential Security Controls
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) MFA represents one of the most cost-effective security investments available. With implementation costs typically ranging from $1-$3 per user per month, MFA can prevent up to 99.9% of automated attacks, as noted in Microsoft’s “One simple action you can take to prevent 99.9 percent of attacks on your accounts.”8 The return on investment is immediate and substantial, making it a cornerstone of any budget-conscious security strategy.
2. Regular Software Updates and Patch Management Maintaining current software versions costs virtually nothing but provides significant security benefits. Automated patch management systems can be implemented for minimal cost while dramatically reducing the attack surface. Organizations should prioritize:
- Operating system updates
- Application patches
- Security software updates
- Firmware updates for network devices
3. Email Security Solutions Given that phishing remains one of the most common attack vectors, investing in email security solutions provides excellent value. Cloud-based email security services typically cost $2-$5 per user per month while blocking the vast majority of malicious emails.
Cloud-Based Security Services
Software as a Service (SaaS) Security Solutions Cloud-based security services offer several advantages for budget-conscious organizations:
- Lower upfront costs: No need for expensive hardware or software licenses
- Automatic updates: Continuous protection without manual intervention
- Scalability: Pay only for what you use
- Expertise included: Access to security expertise without hiring specialists
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Modern EDR solutions provide comprehensive endpoint protection at a fraction of traditional enterprise security costs. These solutions typically cost $3-$8 per endpoint per month and offer:
- Real-time threat detection
- Automated response capabilities
- Forensic investigation tools
- Continuous monitoring
Open Source and Free Security Tools
Network Security Several open source tools can provide enterprise-grade network security without licensing costs:
- pfSense: Comprehensive firewall and routing platform
- Suricata: Network threat detection engine
- Zeek: Network security monitoring platform
Vulnerability Management Free vulnerability scanning tools can help identify security gaps:
- OpenVAS: Comprehensive vulnerability scanner
- Nessus Home: Free for personal use with limited commercial applications
- OWASP ZAP: Web application security testing
Implementation Strategies
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-3)
Priority Actions:
- Implement MFA across all systems
- Establish automated patch management
- Deploy basic email security
- Conduct security awareness training
Budget Allocation:
- MFA implementation: $500-$1,500
- Email security: $1,000-$3,000 annually
- Training materials: $200-$500
- Total Phase 1 Investment: $1,700-$5,000
Phase 2: Enhanced Protection (Months 4-6)
Priority Actions:
- Deploy endpoint detection and response
- Implement backup and recovery solutions
- Establish incident response procedures
- Regular security assessments
Budget Allocation:
- EDR solution: $2,000-$6,000 annually
- Backup services: $1,000-$3,000 annually
- Security assessment: $2,000-$5,000
- Total Phase 2 Investment: $5,000-$14,000
Phase 3: Advanced Capabilities (Months 7-12)
Priority Actions:
- Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Deploy advanced threat detection
- Establish security governance framework
- Regular penetration testing
Budget Allocation:
- SIEM solution: $3,000-$8,000 annually
- Advanced threat detection: $2,000-$5,000 annually
- Penetration testing: $3,000-$8,000
- Total Phase 3 Investment: $8,000-$21,000
Leveraging Managed Security Services
The MSP Advantage
Given that less than 30% of SMBs manage security in-house, partnering with a Managed Security Service Provider (MSP) offers several advantages:
Cost Efficiency:
- Access to enterprise-grade security tools without capital investment
- Shared expertise costs across multiple clients
- Predictable monthly expenses
- Reduced need for internal security staff
24/7 Monitoring:
- Continuous threat detection and response
- Incident response capabilities
- Regular security updates and maintenance
- Compliance support
Selecting the Right MSP
Key Criteria:
- Industry expertise: Experience with your specific industry and regulatory requirements
- Technology partnerships: Relationships with leading security vendors
- Local presence: Understanding of Australian regulatory landscape
- Scalability: Ability to grow with your business
- Cost transparency: Clear pricing models and service level agreements
Maximizing ROI Through Automation
AI-Powered Security Solutions
The integration of artificial intelligence in security operations represents a paradigm shift in cost-effective protection. Organizations utilizing AI and automation in their security strategies have demonstrated significant cost savings:
Key Benefits:
- Reduced false positives: AI algorithms can distinguish between legitimate activities and genuine threats
- Faster response times: Automated incident response can contain threats within minutes
- Predictive capabilities: AI can identify potential security issues before they become incidents
- Resource optimization: Automated systems can manage routine security tasks, freeing human resources for strategic initiatives
Implementation Considerations
Starting with Automation:
- Email filtering: Automated phishing detection and blocking
- Patch management: Automated update deployment
- Backup verification: Automated backup testing and reporting
- Log analysis: Automated security event correlation
Compliance and Cost Management
Regulatory Alignment
For Australian businesses, aligning security investments with regulatory requirements can provide dual benefits: enhanced security and compliance cost management.
Key Frameworks:
- Australian Privacy Principles (APPs): Data protection requirements
- Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) scheme: Incident reporting obligations
- Australian Government Information Security Manual (ISM): Security control framework
- Industry-specific regulations: Sector-specific compliance requirements
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Measuring Security ROI:
- Risk reduction: Quantify the reduction in potential breach costs
- Operational efficiency: Calculate time savings from automated processes
- Compliance costs: Compare security investments to potential regulatory fines
- Business continuity: Assess the value of maintained operations during incidents
Future-Proofing Your Security Investment
Emerging Threats and Budget Considerations
Artificial Intelligence Threats: Many SMBs believe AI increases the need for additional security controls. However, budget-conscious organizations can address these emerging threats through:
- AI-powered security tools: Leverage AI for defense rather than viewing it solely as a threat
- Data governance frameworks: Implement proper data classification and protection
- Employee training: Educate staff on AI-related security risks
Remote Work Security: With many SMBs employing remote or hybrid workers, securing distributed workforces requires cost-effective solutions:
- Zero Trust architecture: Implement identity-based security models
- Cloud-based security: Utilize SaaS solutions for remote access protection
- Endpoint management: Deploy mobile device management solutions
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Key Performance Indicators
Security Metrics:
- Mean Time to Detection (MTTD): Average time to identify security incidents
- Mean Time to Response (MTTR): Average time to contain and resolve incidents
- Security training completion rates: Percentage of staff completing security awareness training
- Vulnerability remediation time: Time to patch identified vulnerabilities
Financial Metrics:
- Cost per protected asset: Security spending relative to protected resources
- Return on security investment: Financial benefits relative to security spending
- Incident cost avoidance: Estimated costs prevented through security measures
Continuous Improvement Process
Regular Assessment Cycle:
- Quarterly reviews: Assess security posture and budget utilization
- Annual penetration testing: Validate security control effectiveness
- Threat landscape updates: Adapt security measures to emerging threats
- Cost optimization: Identify opportunities for improved efficiency
Conclusion
Implementing cost-effective security solutions for limited budgets requires a strategic approach that balances protection needs with financial constraints. By focusing on high-impact, low-cost security measures and leveraging automation, cloud services, and managed security providers, organizations can achieve robust security postures without overwhelming their budgets.
The key to success lies in understanding that security is not a destination but a journey of continuous improvement. Starting with foundational security controls, gradually building capabilities, and maintaining a focus on the most critical assets and threats will enable organizations to develop sustainable, cost-effective security programs.
As cyber threats continue to evolve and the cost of data breaches reaches new heights, the question is not whether organizations can afford to invest in security, but whether they can afford not to. The strategies and solutions outlined in this guide provide a roadmap for building resilient, budget-conscious security programs that protect what matters most while enabling business growth and success.
References
- Microsoft Security. New research: Small and medium business (SMB) cyberattacks are frequent and costly. https://cdn-dynmedia-1.microsoft.com/is/content/microsoftcorp/microsoft/final/en-us/microsoft-brand/documents/SMBCybersecurity-Report-Final.pdf ↩︎
- Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC). (2024). Annual Cyber Threat Report 2023-2024. Australian Signals Directorate (ASD). https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/view-all-content/reports-and-statistics/annual-cyber-threat-report-2023-2024 ↩︎
- IBM. (2024). Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024. https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach ↩︎
- Microsoft. (2024). Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2024. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/security-insider/intelligence-reports/microsoft-digital-defense-report-2024 ↩︎
- Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC). (2024). Annual Cyber Threat Report 2023-2024. Australian Signals Directorate (ASD). https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/view-all-content/reports-and-statistics/annual-cyber-threat-report-2023-2024 ↩︎
- Scott W. (2024). 7 cybersecurity trends and tips for small and medium businesses to stay protected. Microsoft. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/blog/2024/10/31/7-cybersecurity-trends-and-tips-for-small-and-medium-businesses-to-stay-protected/ ↩︎
- IBM. (2024). Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024. https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach ↩︎
- Melanie M. (2019). One simple action you can take to prevent 99.9 percent of attacks on your accounts. Microsoft. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/blog/2019/08/20/one-simple-action-you-can-take-to-prevent-99-9-percent-of-account-attacks/ ↩︎
At Christian Sajere Cybersecurity and IT Infrastructure, we understand that robust security shouldn’t strain your budget. Our cost-effective solutions help Australian businesses maximize protection while minimizing expenses. Let us help you build a security program that fits your budget and protects your future.
Related Blog Posts
- Azure Security Best Practices for Australian Businesses: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
- Tabletop Exercises: Testing Your Incident Response Plan
- BGP Security: Protecting Your Internet Routing
- Data-Centric Security Architecture: Building Resilience Through Data-Focused Protection
- Network Security Zoning and Segmentation Design: Building Resilient Digital Perimeters in 2025
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Communities and Frameworks
- Healthcare Information Security: Australian Privacy Requirements


