In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity has become a critical business imperative rather than a mere IT concern. As organisations increasingly rely on digital infrastructure, the complexity and sophistication of cyber threats continue to escalate, creating significant challenges for businesses attempting to manage security internally. The strategic decision of whether to outsource security operations to a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) has become a pivotal consideration for organisations across Australia and globally.
The managed security services market reflects this growing demand, with industry analysts projecting substantial growth in the coming years. According to market research by MarketsandMarkets in “Managed Security Services Market”1, the global managed security services market, valued at $27.2 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a 15.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2023 to 2030. This explosive growth underscores the increasing recognition among businesses that outsourcing security operations can provide significant strategic advantages.
The Australian cybersecurity landscape presents unique challenges and opportunities. The Australian Signals Directorate’s Australian Cyber Security Centre (ASD’s ACSC) plays a crucial role in this ecosystem, as it leads the Australian Government’s efforts on cyber security, bringing together capabilities to improve the cyber resilience of the Australian community and help make Australia the most secure place to connect online. This national focus on cybersecurity excellence creates both opportunities and expectations for businesses operating in the Australian market.
The Current State of Cybersecurity Threats
The cybersecurity threat landscape has become increasingly complex and costly for organisations worldwide. Recent research from IBM reveals alarming trends in data breach costs and frequency. According to the Cost of a Data Breach Report 20242 by IBM, the global average cost of a data breach in 2024 reached USD 4.88 million, marking a 10% increase from the previous year and the highest figure recorded to date. This rising cost of breaches emphasises the critical importance of implementing robust security measures.
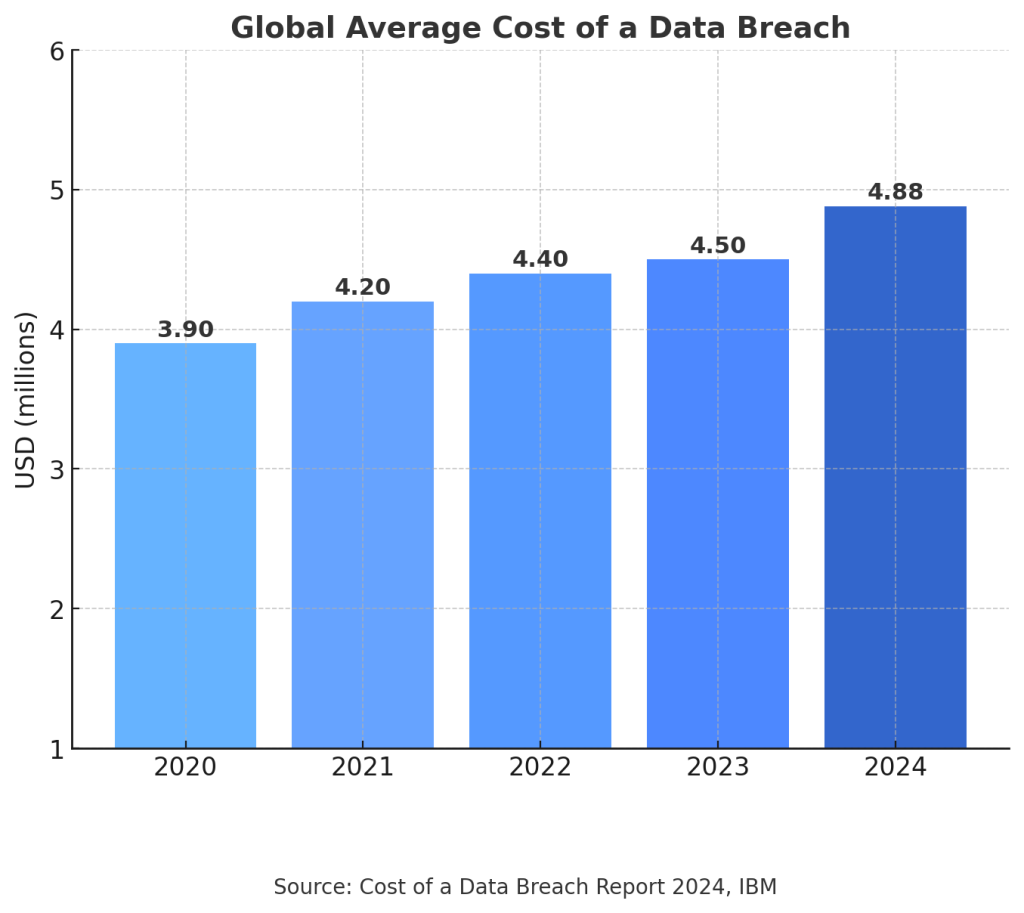
The threat environment is characterised by several key factors that make internal security management increasingly challenging. Cybercriminals are leveraging advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, to develop more sophisticated attack vectors. Ransomware attacks have become more targeted and destructive, while supply chain attacks have demonstrated the interconnected nature of modern security risks.
Australian businesses face particular challenges in this environment. The geographic isolation of many Australian organisations can create unique vulnerabilities, while the increasing digitalisation of traditional industries has expanded the attack surface for potential threats. The Australian Cyber Security Centre’s role becomes particularly important in this context, as it provides national coordination and intelligence sharing to help organisations understand and respond to emerging threats.
The skills shortage in cybersecurity further compounds these challenges. Finding and retaining qualified security professionals has become increasingly difficult, with many organisations struggling to build comprehensive internal security teams. This talent gap has created a significant driver for the growth of managed security services, as organisations seek to access specialised expertise that may not be available internally.
Understanding Managed Security Services
Managed Security Services represent a comprehensive approach to outsourcing an organisation’s cybersecurity operations to specialised providers. These services encompass a wide range of security functions, from basic monitoring and alerting to advanced threat hunting and incident response. The core value proposition of managed security services lies in providing organisations with access to enterprise-grade security capabilities without the need to build and maintain these capabilities internally.
Modern MSSPs offer sophisticated security operations centres (SOCs) that provide around-the-clock monitoring and response capabilities. These facilities leverage advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automated response systems, to detect and respond to threats in real-time. The scale and sophistication of these operations often exceed what individual organisations can achieve internally, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises.
The service portfolio of modern MSSPs typically includes several key components. Continuous monitoring forms the foundation, with security analysts watching for suspicious activities across an organisation’s digital infrastructure. Threat intelligence services provide contextual information about emerging threats and attack patterns. Incident response capabilities ensure rapid containment and remediation when security incidents occur. Many providers also offer vulnerability management, compliance reporting, and strategic security consulting services.
IBM, as a leading provider in this space, offers around-the-clock monitoring, management and response to advanced threats, risks, and compliance needs through its managed security services, as explained in “Managed Security Services (MSS)”3. This comprehensive approach reflects the industry trend toward providing end-to-end security solutions rather than point products.
The technology infrastructure supporting modern managed security services has evolved significantly. Cloud-based security platforms enable rapid deployment and scaling of security services. Advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities help identify subtle indicators of compromise that might be missed by traditional security tools. Integration capabilities allow MSSPs to work seamlessly with existing organisational infrastructure and processes.
Key Benefits of Outsourcing Security Operations
The decision to outsource security operations delivers several strategic advantages that extend beyond simple cost considerations. Understanding these benefits is crucial for organisations evaluating their security strategy options.
Access to Specialized Expertise
One of the most significant advantages of managed security services is access to specialised cybersecurity expertise. Building an internal security team with comprehensive skills across all security domains requires substantial investment and ongoing training. MSSPs employ teams of certified security professionals who specialise in different aspects of cybersecurity, from threat analysis to incident response. This depth of expertise is particularly valuable for addressing sophisticated threats that require specialised knowledge and experience.
24/7 Security Operations
Cyber threats operate around the clock, but maintaining internal 24/7 security operations is costly and complex. MSSPs provide continuous monitoring and response capabilities, ensuring that threats are detected and addressed regardless of when they occur. This around-the-clock coverage is particularly important for Australian organisations that may have limited internal resources for after-hours security operations.
Advanced Technology Access
MSSPs invest heavily in cutting-edge security technologies and platforms. Organisations benefit from access to these advanced tools without the capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance costs associated with purchasing and managing these systems internally. The technology stack available through managed services often includes sophisticated threat intelligence platforms, advanced analytics tools, and automated response capabilities that would be prohibitively expensive for individual organisations to implement.
Scalability and Flexibility
Managed security services offer significant scalability advantages. As organisations grow or their security needs evolve, MSSPs can quickly adjust service levels and capabilities to match changing requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable for organisations experiencing rapid growth or seasonal variations in their security needs.
Cost Predictability
Outsourcing security operations provides predictable cost structures that facilitate better budget planning. Rather than managing variable costs associated with hiring, training, and retaining security staff, organisations can work with fixed or predictable service fees. This cost predictability extends to technology costs, as the MSSP manages infrastructure investments and upgrades.
Compliance and Regulatory Support
Many managed security providers offer specialised compliance and regulatory support services. This is particularly valuable for organisations operating in heavily regulated industries or those subject to specific compliance requirements. The expertise and systems provided by MSSPs can significantly simplify compliance reporting and audit processes.
When Outsourcing Makes Strategic Sense
The decision to outsource security operations should be based on careful evaluation of organisational needs, capabilities, and strategic objectives. Several key factors indicate when outsourcing represents the optimal strategic choice.
Limited Internal Security Expertise
Organisations lacking comprehensive internal security expertise are prime candidates for managed security services. The cybersecurity skills shortage makes it increasingly difficult for many organisations to recruit and retain qualified security professionals. Rather than operating with limited internal capabilities, outsourcing provides immediate access to a full team of security experts.
Resource Constraints
Small to medium-sized enterprises often face resource constraints that make building comprehensive internal security capabilities challenging. The investment required for security tools, infrastructure, and personnel can be substantial. Managed security services allow these organisations to access enterprise-grade security capabilities at a fraction of the cost of building internal capabilities.
Rapid Growth or Scaling Requirements
Organisations experiencing rapid growth often find that their security needs evolve faster than their ability to build internal capabilities. Managed security services provide the scalability needed to support rapid growth while maintaining strong security posture. This is particularly relevant for technology companies and other organisations in high-growth sectors.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Industries subject to strict regulatory requirements, such as financial services, healthcare, and government contractors, often benefit significantly from managed security services. MSSPs specialising in these sectors bring deep expertise in regulatory requirements and can provide the documentation and reporting needed for compliance purposes.
Geographic Distribution
Organisations with distributed operations across multiple locations face unique security challenges. Managing security consistently across multiple sites can be complex and expensive. Managed security services provide centralised security operations that can effectively protect distributed organisations.
Critical Infrastructure Protection
Organisations operating critical infrastructure face sophisticated and persistent threats that require advanced security capabilities. The Australian Cyber Security Centre recognises the importance of protecting critical infrastructure, and managed security services can provide the specialised capabilities needed to defend against advanced persistent threats as can be seen in its “Principles of operational technology cyber security,”4 which was released in partnership with CISA, FBI, NSA, and other international partners.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Framework
Developing a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is essential for making informed decisions about security outsourcing. This analysis should consider both direct and indirect costs, as well as quantifiable and intangible benefits.
Direct Cost Considerations
The direct costs of managed security services are typically straightforward to calculate. These include monthly or annual service fees, implementation costs, and any additional charges for premium services or incident response activities. However, organisations should also consider the total cost of ownership, including integration costs, training requirements, and any necessary infrastructure modifications.
Internal Security Costs
Calculating the true cost of internal security operations requires careful consideration of all related expenses. Personnel costs include not only salaries but also benefits, training, certification maintenance, and recruitment expenses. Technology costs encompass initial hardware and software purchases, ongoing licensing fees, maintenance contracts, and regular upgrades. Infrastructure costs include data centre space, power, cooling, and network connectivity requirements.
Opportunity Cost Analysis
One of the most significant but often overlooked factors in the cost-benefit analysis is opportunity cost. Internal security teams represent a significant investment in human capital that could potentially be deployed in other areas of the business. By outsourcing security operations, organisations can redirect internal resources toward core business activities that directly contribute to revenue generation and competitive advantage.
Risk and Incident Cost Factors
The potential cost of security incidents should be factored into the analysis. With the global average cost of a data breach reaching USD 4.9 million in 2024, according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 20245, the financial impact of inadequate security can be substantial. Managed security services can potentially reduce both the likelihood and impact of security incidents through improved detection, faster response times, and better incident management capabilities.
Quantifying Intangible Benefits
While some benefits of managed security services are difficult to quantify precisely, they can provide significant value. Improved employee productivity resulting from reduced security-related disruptions, enhanced customer confidence due to better security posture, and improved regulatory compliance can all contribute to organisational value in ways that may not be immediately apparent in traditional cost-benefit calculations.
Risk Considerations and Mitigation Strategies
While managed security services offer significant benefits, organisations must also carefully consider and mitigate potential risks associated with outsourcing critical security functions.
Data Privacy and Confidentiality Concerns
Outsourcing security operations necessarily involves sharing sensitive information with third-party providers. Organisations must carefully evaluate the data handling practices, security controls, and privacy protections offered by potential MSSPs. This is particularly important for organisations handling sensitive customer data, intellectual property, or other confidential information.
Academic research has highlighted this concern, noting that firms may develop in-house security protection for the fear of leaking data by an MSSP, especially for core business like enterprise resource planning. This research emphasises the importance of carefully evaluating data protection measures when considering outsourcing options.
Vendor Dependency and Lock-in Risks
Outsourcing security operations can create dependency on specific vendors and technologies. Organisations should carefully evaluate contract terms, data portability options, and exit strategies to avoid unwanted vendor lock-in situations. Maintaining some level of internal security capability can help mitigate these risks while still benefiting from outsourced services.
Service Level and Performance Risks
The effectiveness of managed security services depends heavily on the provider’s ability to deliver consistent, high-quality services. Organisations should establish clear service level agreements (SLAs) that define performance expectations, response times, and escalation procedures. Regular performance monitoring and review processes help ensure that service quality meets organisational requirements.
Compliance and Regulatory Risks
While managed security services can enhance compliance capabilities, they can also introduce compliance risks if not properly managed. Organisations remain ultimately responsible for regulatory compliance, even when security operations are outsourced. Clear contractual arrangements and regular compliance audits help mitigate these risks.
Communication and Coordination Challenges
Effective security operations require close coordination between internal teams and external providers. Communication challenges, time zone differences, and cultural factors can impact the effectiveness of this coordination. Establishing clear communication protocols, regular reporting procedures, and escalation pathways helps address these challenges.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries face unique security challenges and regulatory requirements that influence the decision to outsource security operations.
Financial Services
The financial services sector faces some of the most sophisticated cyber threats and strictest regulatory requirements. Banks, insurance companies, and other financial institutions must comply with regulations such as the Prudential Regulation Authority’s (PRA) “Prudential Standard CPS 234 Information Security”6 requirements and industry standards like PCI DSS. Managed security services can provide the specialised expertise and compliance capabilities needed to meet these requirements while defending against advanced threats.
Healthcare
Healthcare organisations handle sensitive patient data and face increasing cyber threats targeting medical devices and electronic health records. Compliance with privacy regulations and the critical nature of healthcare operations create unique requirements for security services. MSSPs specialising in healthcare can provide the necessary expertise and compliance support while ensuring that security measures don’t interfere with patient care.
Government and Public Sector
Government agencies and public sector organisations face unique security challenges, including nation-state threats and strict data sovereignty requirements. The Australian Government’s focus on cybersecurity, coordinated through the Australian Cyber Security Centre, creates both opportunities and requirements, such as the “Protecting Against Cyber Threats to Managed Service Providers and their Customers”7 for enhanced security capabilities. Managed security services can help government organisations access advanced capabilities while maintaining appropriate security clearances and data handling procedures.
Manufacturing and Critical Infrastructure
Manufacturing organisations and critical infrastructure operators face increasing threats targeting operational technology (OT) systems. These threats can have physical consequences beyond traditional data breaches. MSSPs with expertise in industrial control systems and operational technology can provide specialised protection for these environments.
Selecting the Right Managed Security Service Provider
Choosing the appropriate MSSP is crucial for the success of any security outsourcing initiative. Several key factors should guide this selection process.
Technical Capabilities and Expertise
Evaluating the technical capabilities of potential MSSPs requires careful assessment of their technology platforms, analytical capabilities, and staff expertise. Organisations should look for providers with advanced security operations centres, sophisticated threat intelligence capabilities, and proven experience in their specific industry sector.
Geographic Presence and Data Sovereignty
For Australian organisations, geographic presence and data sovereignty considerations are particularly important. Providers with local presence and data centres can offer better response times and compliance with Australian data protection requirements. Understanding where data will be stored and processed is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and managing risk.
Industry Experience and Specialisation
MSSPs with specific industry experience bring valuable contextual knowledge about sector-specific threats, regulatory requirements, and operational considerations. This specialisation can significantly enhance the effectiveness of security services and reduce the learning curve for new engagements.
Service Portfolio and Integration Capabilities
The breadth and depth of services offered by potential providers should align with organisational needs. Some organisations may require comprehensive security services, while others may need specific capabilities to complement existing internal resources. Integration capabilities are particularly important for organisations with existing security investments.
Financial Stability and Business Continuity
The financial stability of potential MSSPs is an important consideration, as security services are critical to ongoing operations. Organisations should evaluate the provider’s financial health, business continuity plans, and backup service arrangements to ensure service continuity.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful implementation of managed security services requires careful planning and execution. Several best practices can help ensure successful outcomes.
Comprehensive Requirements Assessment
Before engaging with potential providers, organisations should conduct a thorough assessment of their security requirements, existing capabilities, and desired outcomes. This assessment should include current threat landscape analysis, regulatory requirements, and integration needs with existing systems and processes.
Phased Implementation Approach
Rather than attempting to outsource all security operations simultaneously, many organisations benefit from a phased approach. Starting with specific services or business units allows for learning and adjustment before expanding the scope of outsourced services.
Clear Communication and Escalation Procedures
Establishing clear communication protocols and escalation procedures is essential for effective managed security services. This includes regular reporting schedules, incident notification procedures, and escalation pathways for different types of security events.
Regular Performance Monitoring and Review
Ongoing monitoring of service performance against established SLAs helps ensure that outsourced services continue to meet organisational needs. Regular reviews provide opportunities to adjust service levels, address emerging requirements, and optimise the relationship with the MSSP.
Maintaining Internal Security Awareness
While outsourcing security operations, organisations should maintain appropriate internal security awareness and capabilities. This includes ensuring that internal staff understand their roles in the security ecosystem and maintaining some level of internal security expertise to effectively manage the relationship with the MSSP.
Future Trends and Considerations
The managed security services market continues to evolve rapidly, driven by changing threat landscapes, technological advancement, and regulatory requirements.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and ML technologies are increasingly being integrated into managed security services to improve threat detection, reduce false positives, and automate response activities. These technologies enable MSSPs to process larger volumes of security data and identify subtle indicators of compromise that might be missed by traditional approaches.
Cloud-Native Security Services
As organisations continue to migrate to cloud environments, managed security services are evolving to provide cloud-native capabilities. This includes specialised monitoring for cloud workloads, container security, and serverless application protection.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
The evolution toward XDR platforms represents a significant trend in managed security services. These platforms provide integrated detection and response capabilities across multiple security domains, including endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and applications.
Regulatory Evolution
The regulatory landscape for cybersecurity continues to evolve, with new requirements for incident reporting, data protection, and security controls. MSSPs must continually adapt their capabilities to help organisations meet these evolving requirements.
Industry Specialisation
The trend toward industry specialisation among MSSPs is expected to continue, with providers developing deeper expertise in specific sectors. This specialisation enables more effective threat detection and response tailored to industry-specific risks and requirements.
Conclusion
The decision to outsource managed security services represents a significant strategic choice that can provide substantial benefits for organisations across various industries. The rapid growth of the managed security services market, projected to grow at a 15.4% compound annual growth rate from 2023 to 2030, reflects the increasing recognition of these benefits among business leaders worldwide.
For Australian organisations, the decision to outsource security operations should be evaluated within the context of the national cybersecurity framework coordinated by the Australian Cyber Security Centre. The ACSC’s mission to make Australia the most secure place to connect online creates both opportunities and expectations for enhanced cybersecurity capabilities across all sectors of the economy.
The key factors favouring outsourcing include access to specialised expertise, 24/7 security operations, advanced technology platforms, scalability, cost predictability, and compliance support. These benefits are particularly valuable for organisations with limited internal security resources, those experiencing rapid growth, or those operating in highly regulated industries.
However, the decision to outsource must be balanced against considerations of data privacy, vendor dependency, service level risks, and the need to maintain appropriate internal security capabilities. Successful outsourcing requires careful provider selection, comprehensive implementation planning, and ongoing performance management.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve and the costs of security incidents continue to rise, managed security services offer a compelling value proposition for many organisations. The key to success lies in carefully evaluating organisational needs, selecting the right provider, and implementing services in a way that enhances rather than replaces critical internal security capabilities.
The future of managed security services will be shaped by advancing technologies, evolving regulatory requirements, and the continued sophistication of cyber threats. Organisations that thoughtfully leverage these services while maintaining appropriate internal capabilities will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly digital and interconnected business environment.
References
- MarketsandMarkets, “Managed Security Services Market”, 2024 https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/managed-security-services-market-5918403.html ↩︎
- IBM, “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024”, https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/cost-of-a-data-breach-2024-financial-industry ↩︎
- IBM, “Managed Security Services (MSS)”, https://www.ibm.com/services/managed-security ↩︎
- Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), “Principles of operational technology cyber security,” 2024 https://www.cyber.gov.au/sites/default/files/2024-10/principles_of_operational_technology_cyber_security.pdf ↩︎
- IBM, “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024”, https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach ↩︎
- Australian Government, Federal Register of Legislation, “Prudential Standard CPS 234 Information Security”, 2019 https://www.legislation.gov.au/F2018L01745/latest/text ↩︎
- Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), “Protecting Against Cyber Threats to Managed Service Providers and their Customers”, 2022 https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/advisories/protecting-against-cyber-threats-managed-service-providers-and-their-customers ↩︎
At Christian Sajere Cybersecurity and IT Infrastructure, we understand that choosing the right managed security approach is critical for your organisation’s success. Our expert team specialises in helping Australian businesses navigate complex security decisions and implement solutions that deliver real protection. Let us help you determine when outsourcing makes sense for your unique environment.
Related Blog Posts
- Mapping Security Controls to Business Requirements: A Strategic Approach to Cybersecurity Alignment
- GDPR Compliance for Australian Companies with EU Customers: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
- Developing Cyber Threat Intelligence Requirements: A Strategic Framework for Modern Organizations
- Cybersecurity Insurance for Australian SMBs: A Critical Shield Against Rising Cyber Threats
- Securing Data Pipelines for AI Training: A Comprehensive Guide for Australian Enterprises
- Hash Functions and Their Applications in Security
- PCI DSS: Implementation Guide for Australian Merchants


